capabilities on par with wired networks. According
to the report, Wi-Fi connection speeds originating from
dual-mode (Wi-Fi and cellular) mobile devices will more
than double by 2022 globally. The average Wi-Fi network
connection speed of 24.4 Mb/s in 2017 will exceed
54.2 Mb/s by 2022.
Wi-Fi Networks Need to Support
the Growth of Application Traffic
Recent wireless standard amendments (IEEE 802.11ac,
802.11ax, and 802.11ad) are true wired complements,
capable of providing the bandwidths typically associated
with cabled devices only. This also includes highdefinition
(HD) video. Cisco’s November 2018 updated
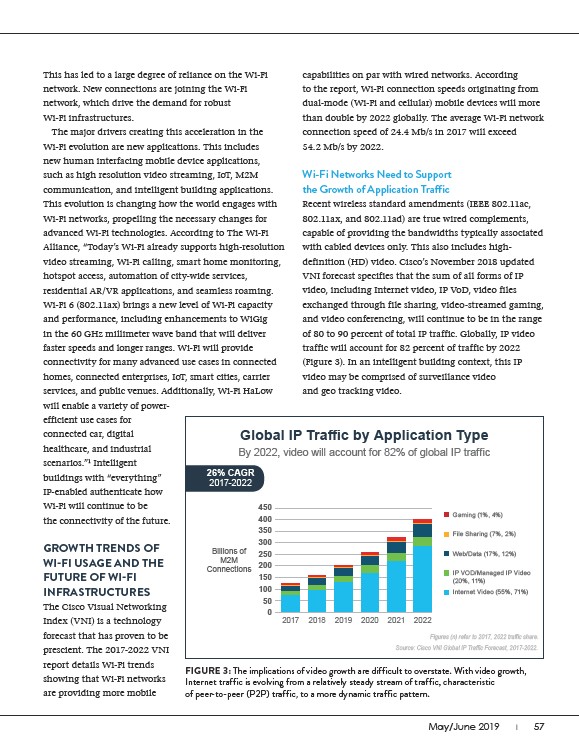
VNI forecast specifies that the sum of all forms of IP
video, including Internet video, IP VoD, video files
exchanged through file sharing, video-streamed gaming,
and video conferencing, will continue to be in the range
of 80 to 90 percent of total IP traffic. Globally, IP video
traffic will account for 82 percent of traffic by 2022
(Figure 3). In an intelligent building context, this IP
video may be comprised of surveillance video
and geo tracking video.
����������������������������������������������������������������������
By 2022, video will account for 82% of global IP traffic
Gaming (1%, 4%)
File Sharing (7%, 2%)
Web/Data (17%, 12%)
IP VOD/Managed IP Video
(20%, 11%)
Internet Video (55%, 71%)
2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022
May/June 2019 I 57
This has led to a large degree of reliance on the Wi-Fi
network. New connections are joining the Wi-Fi
network, which drive the demand for robust
Wi-Fi infrastructures.
The major drivers creating this acceleration in the
Wi-Fi evolution are new applications. This includes
new human interfacing mobile device applications,
such as high resolution video streaming, IoT, M2M
communication, and intelligent building applications.
This evolution is changing how the world engages with
Wi-Fi networks, propelling the necessary changes for
advanced Wi-Fi technologies. According to The Wi-Fi
Alliance, “Today’s Wi-Fi already supports high-resolution
video streaming, Wi-Fi calling, smart home monitoring,
hotspot access, automation of city-wide services,
residential AR/VR applications, and seamless roaming.
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) brings a new level of Wi-Fi capacity
and performance, including enhancements to WiGig
in the 60 GHz millimeter wave band that will deliver
faster speeds and longer ranges. Wi-Fi will provide
connectivity for many advanced use cases in connected
homes, connected enterprises, IoT, smart cities, carrier
services, and public venues. Additionally, Wi-Fi HaLow
will enable a variety of power-
efficient use cases for
connected car, digital
healthcare, and industrial
scenarios.”1 Intelligent
buildings with “everything”
26% CAGR
2017-2022
IP-enabled authenticate how
Wi-Fi will continue to be
450
the connectivity of the future.
400
350
GROWTH TRENDS OF
300
Billions of
250
WI-FI USAGE AND THE
M2M
Connections
200
FUTURE OF WI-FI
150
INFRASTRUCTURES
100
50
The Cisco Visual Networking
0
Index (VNI) is a technology
forecast that has proven to be
prescient. The 2017-2022 VNI
report details Wi-Fi trends
showing that Wi-Fi networks
are providing more mobile
Figures (n) refer to 2017, 2022 traffic share.
Source: Cisco VNI Global IP Traffic Forecast, 2017-2022.
FIGURE 3: The implications of video growth are difficult to overstate. With video growth,
Internet traffic is evolving from a relatively steady stream of traffic, characteristic
of peer-to-peer (P2P) traffic, to a more dynamic traffic pattern.