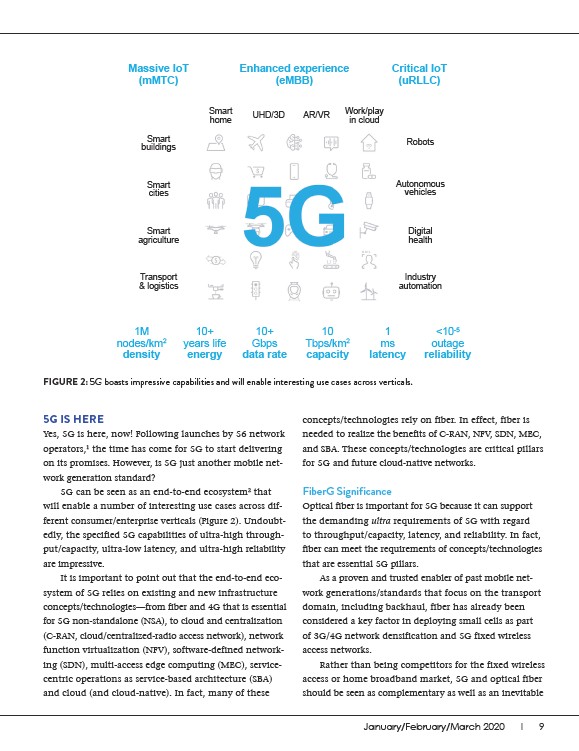
FIGURE 2: 5G boasts impressive capabilities and will enable interesting use cases across verticals.
January/February/March 2020 I 9
5G IS HERE
Yes, 5G is here, now! Following launches by 56 network
operators,1 the time has come for 5G to start delivering
on its promises. However, is 5G just another mobile network
generation standard?
5G can be seen as an end-to-end ecosystem2 that
will enable a number of interesting use cases across different
consumer/enterprise verticals (Figure 2). Undoubtedly,
the specified 5G capabilities of ultra-high throughput/
capacity, ultra-low latency, and ultra-high reliability
are impressive.
It is important to point out that the end-to-end eco-
system of 5G relies on existing and new infrastructure
concepts/technologies—from fiber and 4G that is essential
for 5G non-standalone (NSA), to cloud and centralization
(C-RAN, cloud/centralized-radio access network), network
function virtualization (NFV), software-defined network-
ing (SDN), multi-access edge computing (MEC), service-
centric operations as service-based architecture (SBA)
and cloud (and cloud-native). In fact, many of these
concepts/technologies rely on fiber. In effect, fiber is
needed to realize the benefits of C-RAN, NFV, SDN, MEC,
and SBA. These concepts/technologies are critical pillars
for 5G and future cloud-native networks.
FiberG Significance
Optical fiber is important for 5G because it can support
the demanding ultra requirements of 5G with regard
to throughput/capacity, latency, and reliability. In fact,
fiber can meet the requirements of concepts/technologies
that are essential 5G pillars.
As a proven and trusted enabler of past mobile network
generations/standards that focus on the transport
domain, including backhaul, fiber has already been
considered a key factor in deploying small cells as part
of 3G/4G network densification and 5G fixed wireless
access networks.
Rather than being competitors for the fixed wireless
access or home broadband market, 5G and optical fiber
should be seen as complementary as well as an inevitable
Smart
buildings
Smart
home
Massive IoT
(mMTC)
Enhanced experience
(eMBB)
Critical IoT
(uRLLC)
Work/play
UHD/3D AR/VR in cloud
Robots
Smart
cities
Autonomous
vehicles
Smart
agriculture
Digital
health
Transport
& logistics
Industry
automation
1M
nodes/km2
density
10+
years life
energy
10+
Gbps
data rate
10
Tbps/km2
capacity
<10-5
outage
reliability
1
ms
latency